World population is growing and global architecture, engineering and civil engineering industry are responsible for securing social and economic space for the global population, as well as offer support in maintenance of structures and infrastructure already in use. The industry must seek smarter, more efficient ways of designing and construction, not just with the aim of catching up with global demands, but also to create spaces that are smarter and more resilient. One of those ways in Building Information Modelling – BIM.
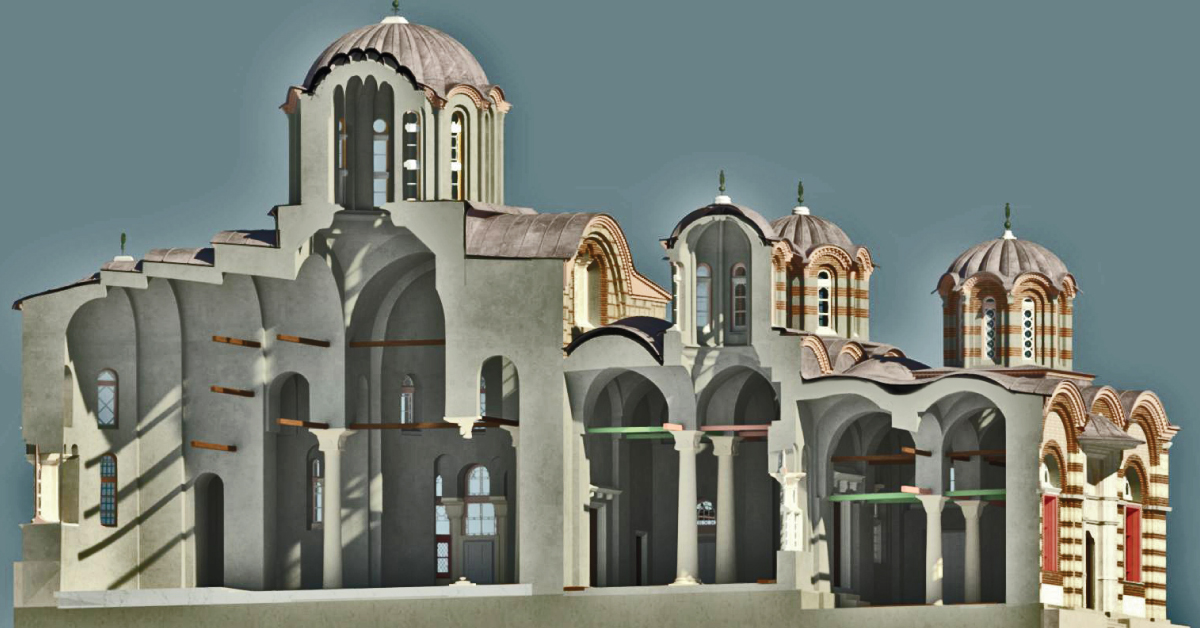
Building Information Modelling (BIM) is a digital representation of physical and functional characteristics of a building (structure). BIM is a resource for sharing knowledge and information regarding a building, thus forming a reliable decision-making base during its entire lifecycle – which implies definition of its existence from the earliest concept design to the demolition of the building.
BIM is a process that begins by creating intelligent 3D models that support different tools and technologies that include generating and managing digital representation of physical and functional characteristics of a certain space. This kind of modelling enables document management, coordination and simulation during the entire lifecycle of the project (plan, design, build, operation and maintenance of the structure).
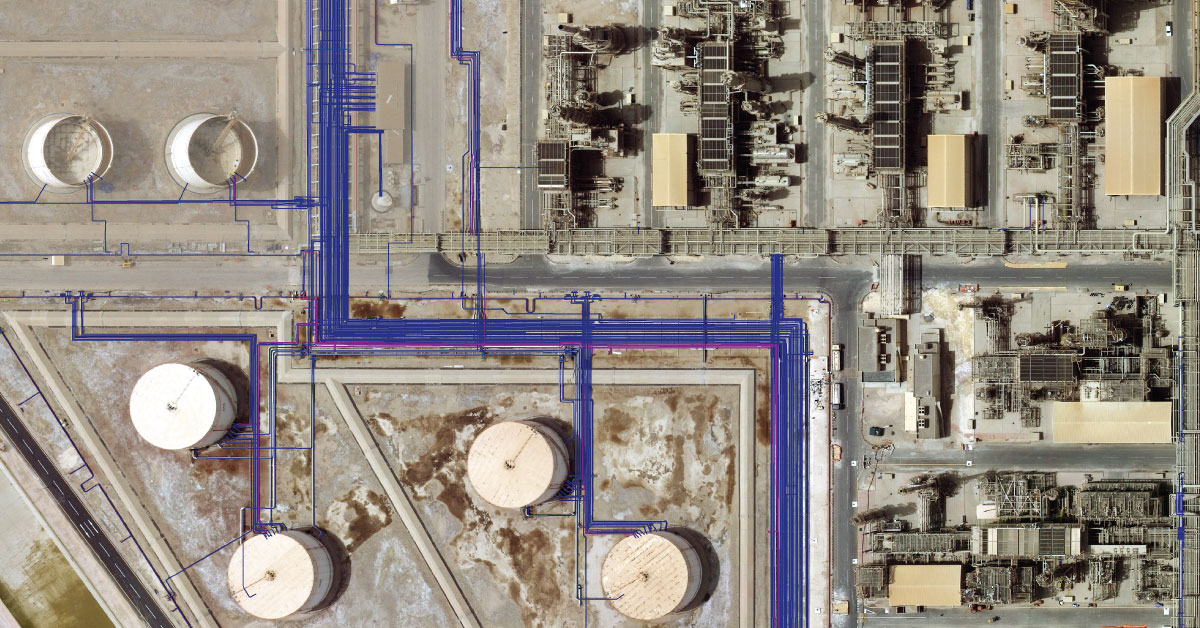
BIM doesn’t just enable engineering teams to work more efficiently, but it also enables acquisition of data collected during the modelling process, which would contribute to operation and maintenance of the structure. BIM data can provide information used in designing and supply on the project, at both city and state level.
BIM software are used by individual designers, business and state agencies that plan, design, build, manage and maintain various physical infrastructures, such as water supply system, sewage, electric power grid, gas pipeline, telecommunications, roads, bridges, portals and tunnels.
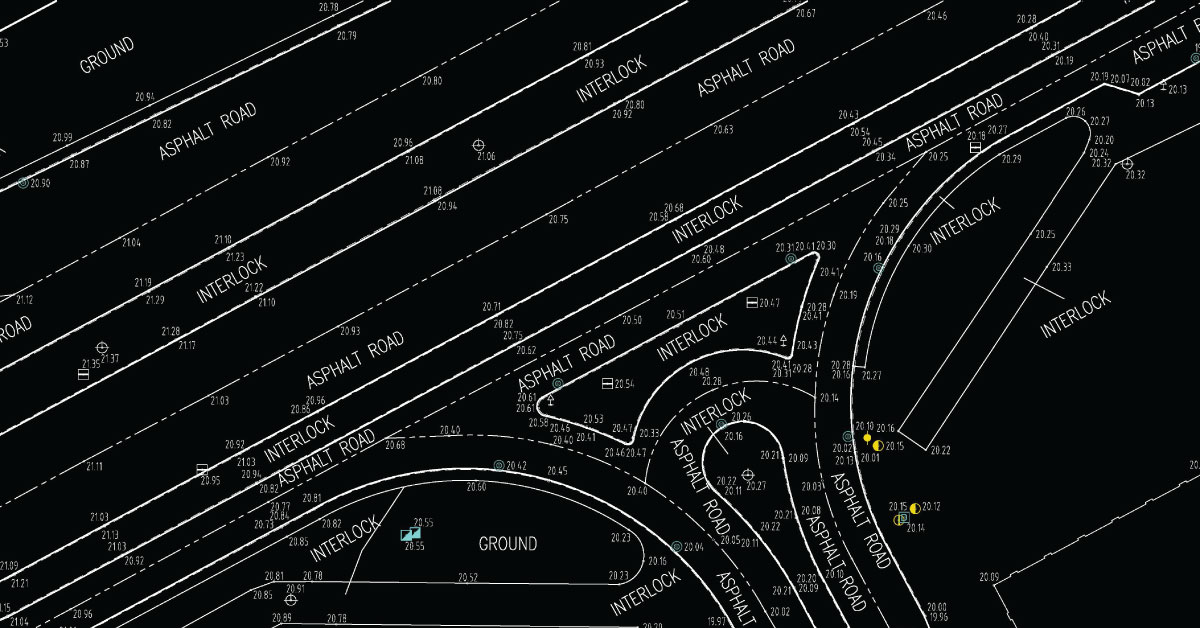
Each detail of the structure is modelled in BMI. The model can be used for analysis to explore the possibilities of the design and to create a visualisation that helps the project stakeholders get a better understanding of how the structure would look like before it’s built.
Model is used to generate construction documentation. Traditional building design relies a lot on 2D technical drawings. BIM also includes more than three dimensions by expanding three primary spatial dimensions (width, height, depth) by time as fourth dimension (4D) and expenses as the fifth dimension (5D). Lately, recommendations can be heard to introduce sixth dimension (6D), which represents environmental aspect and seventh dimension (7D), as the building lifecycle management aspect. Accordingly, BIM covers more than structure geometry. BIM also covers spatial relations, lighting analysis, geographic information, quantity and features of the structure’s components. BIM design tool enables extraction of different views of building model for drawing production and other uses. For professionals involved in the project, BIM enables virtual model of information that can be handled by various engineering teams, contractors, as well as the owner, whereas everyone add to the model discipline-specific data, which are then also exchanged between them. BIM can bridge the loss of information that occurs on the path of project management from construction team to the facility’s owner. BIM concept includes virtual construction of the facility before its actual physical construction with the aim of improving safety, overcoming issues, simulating and analysing potential conflicts.