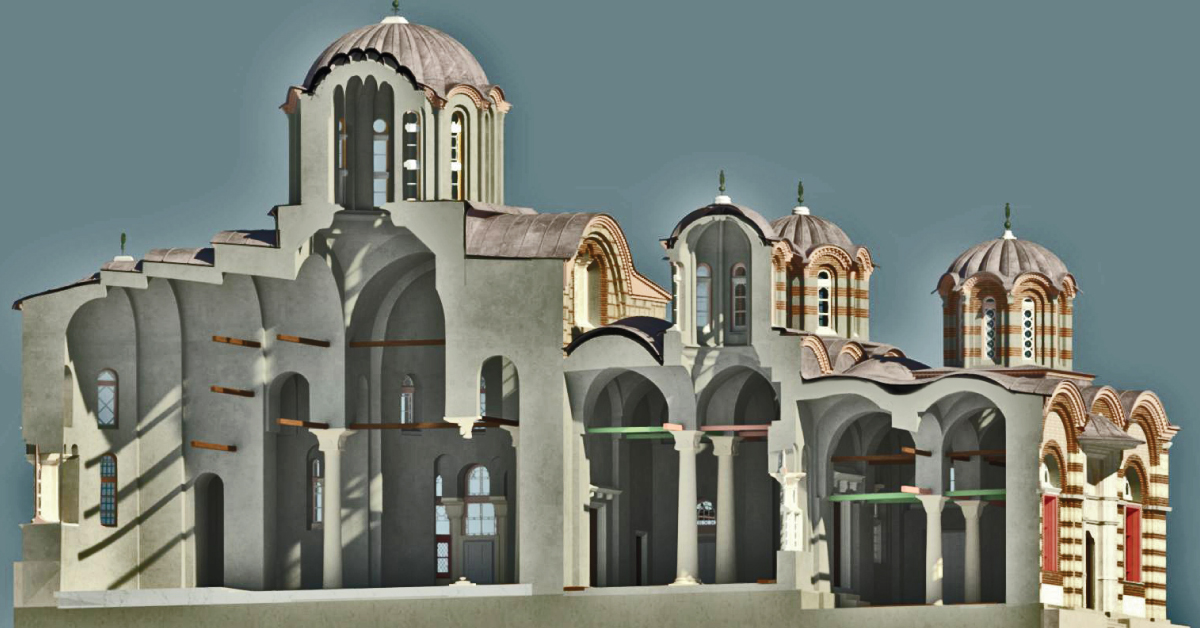
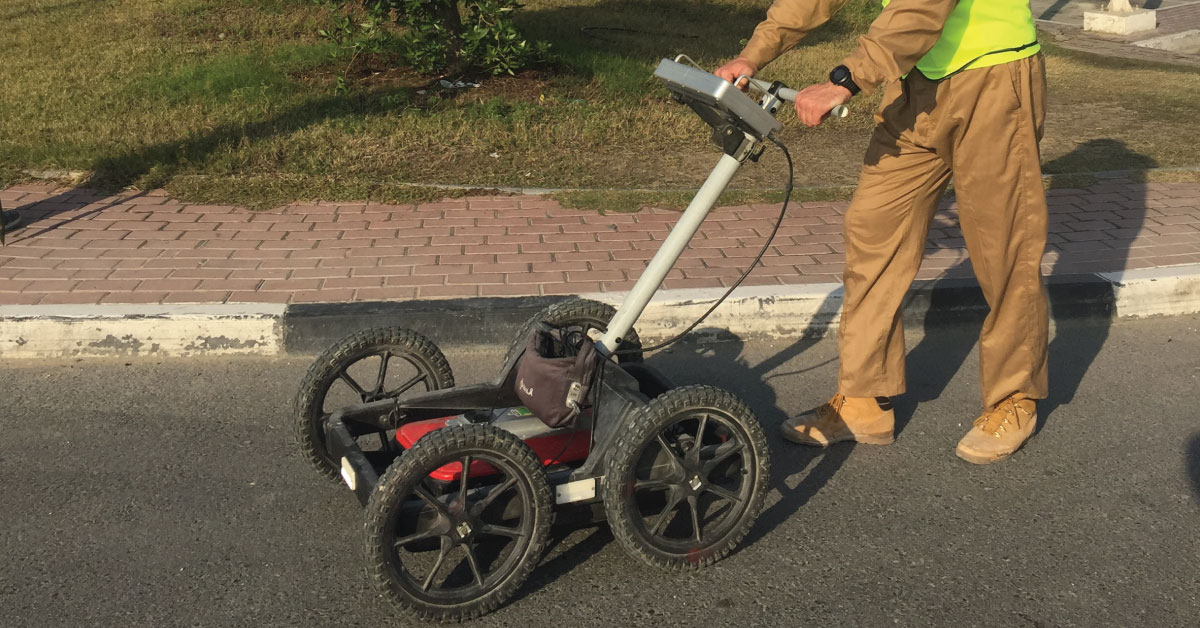
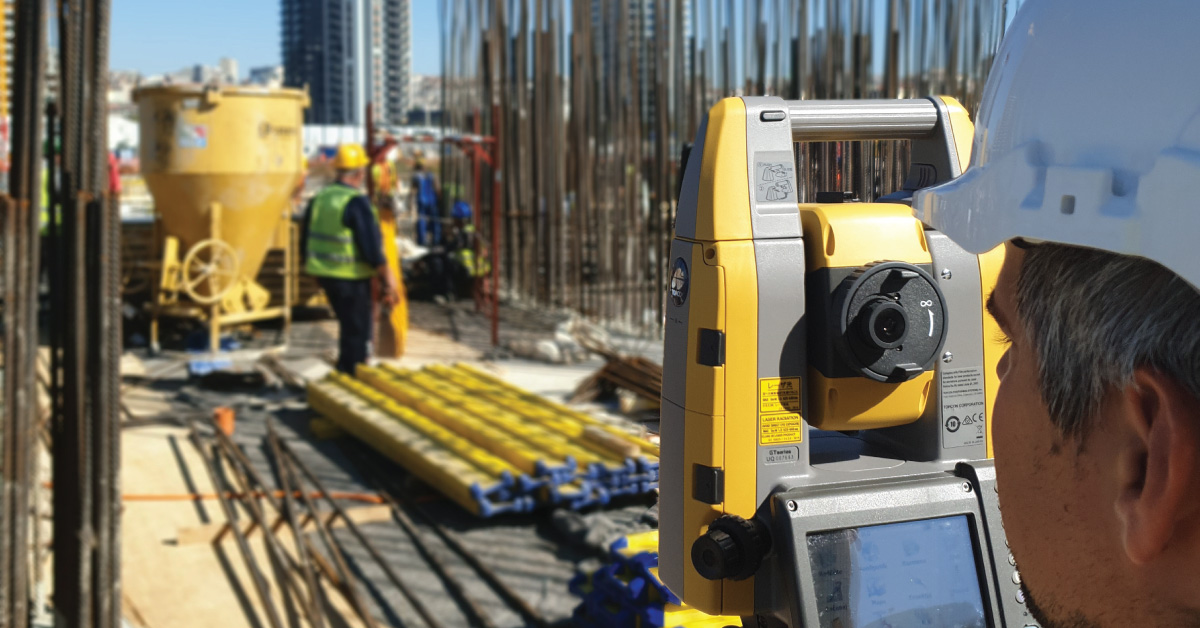
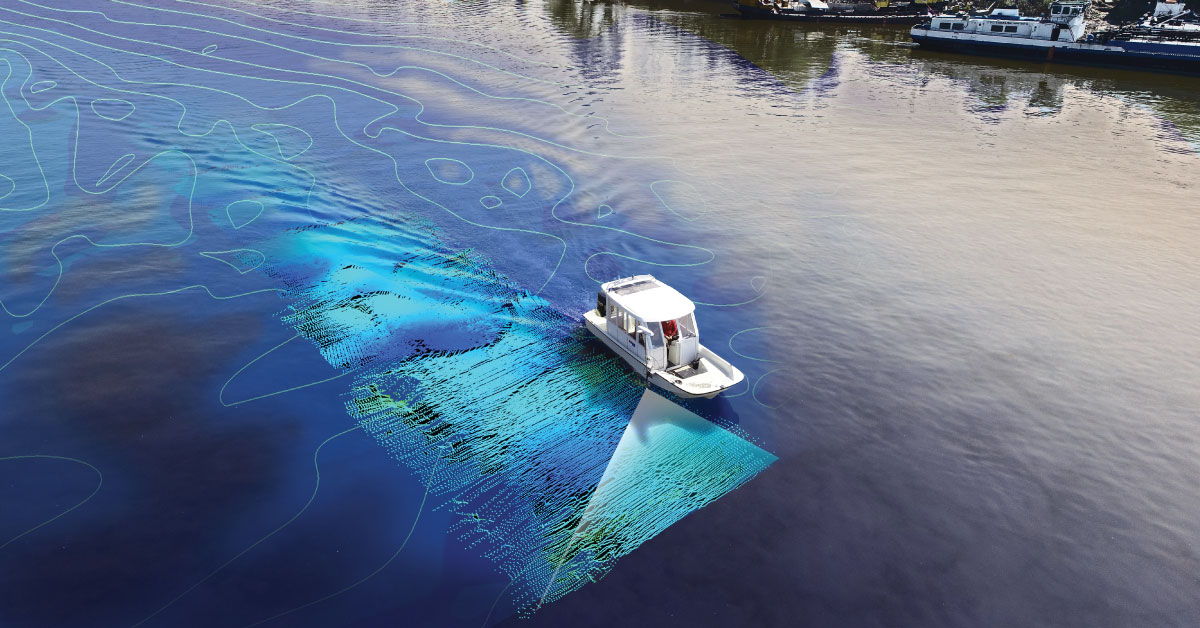
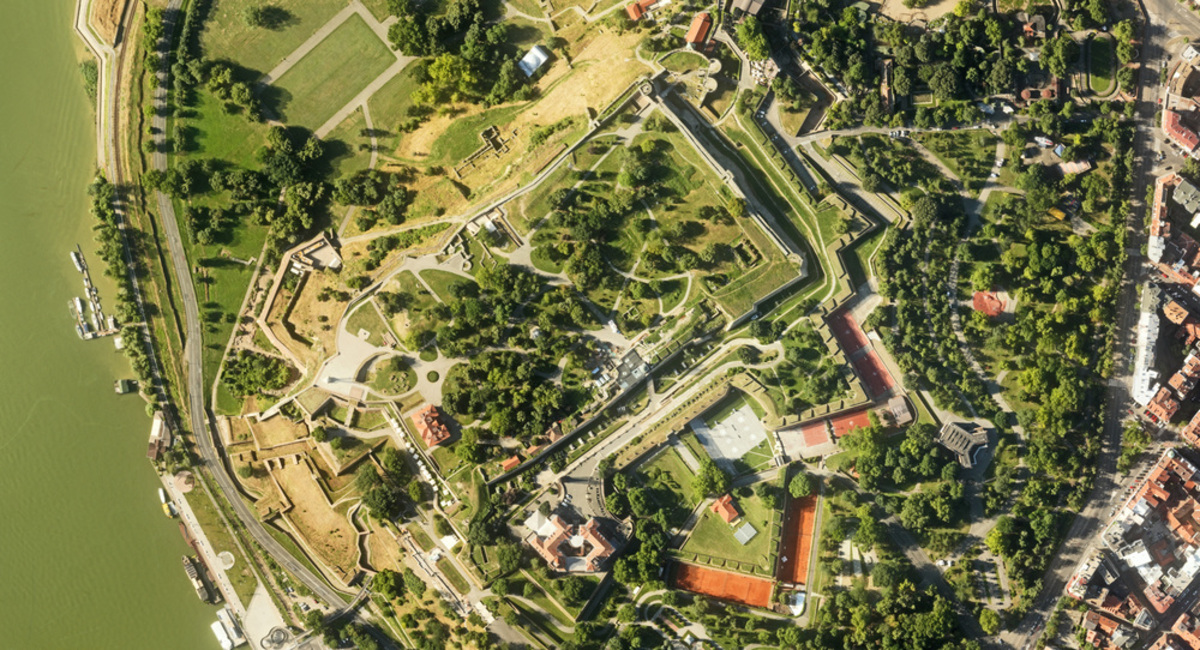
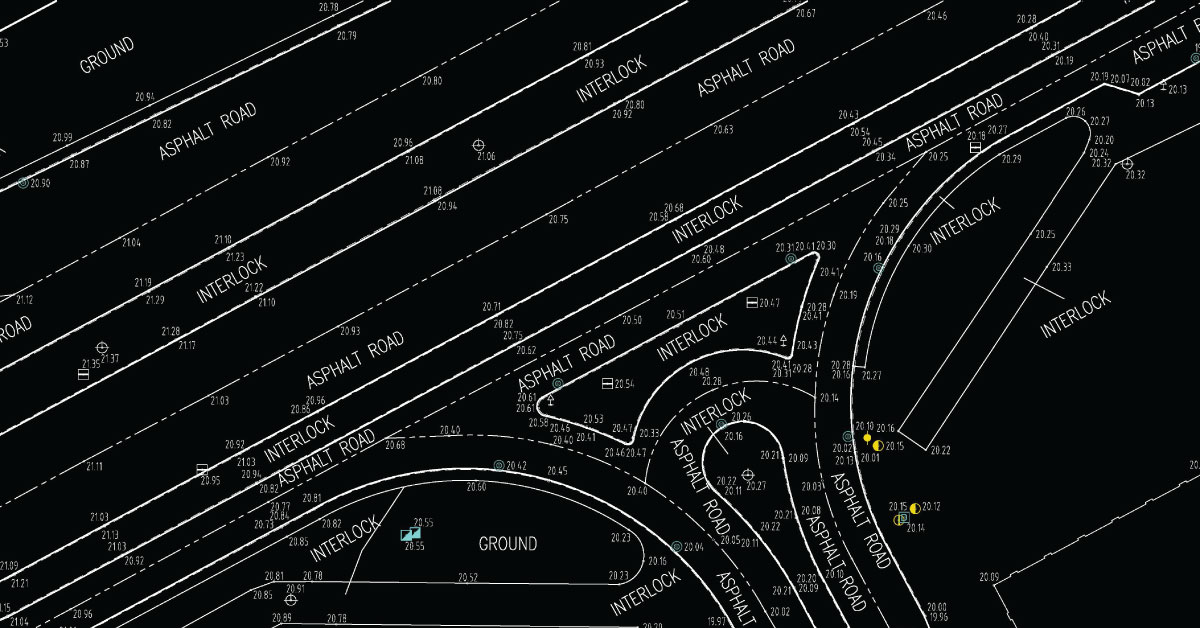
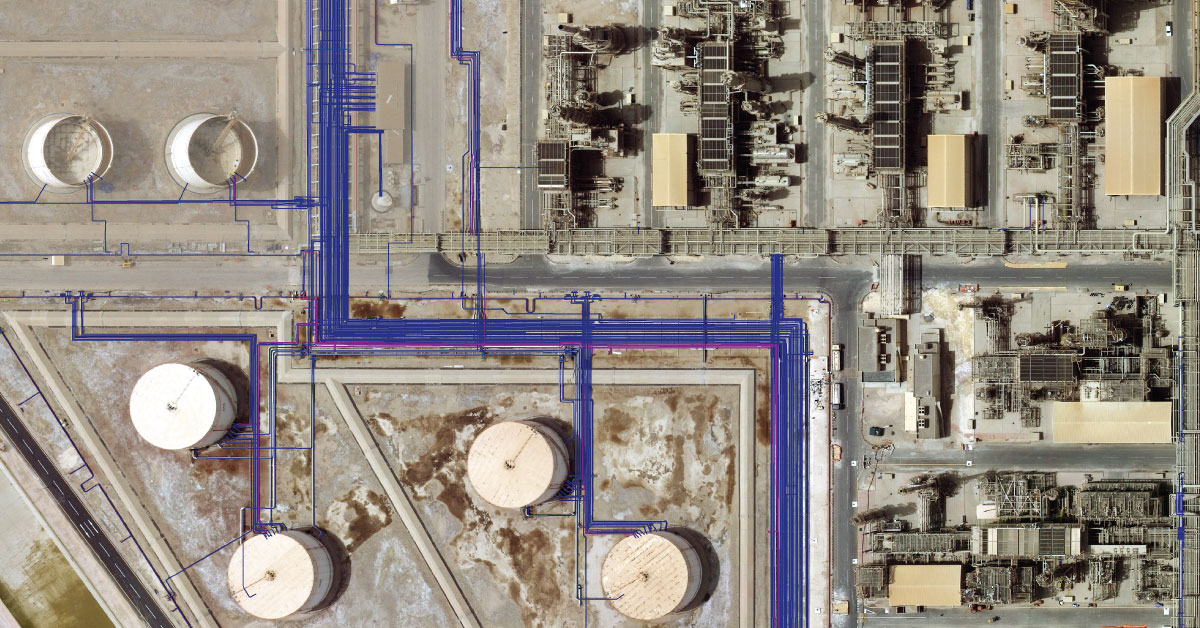
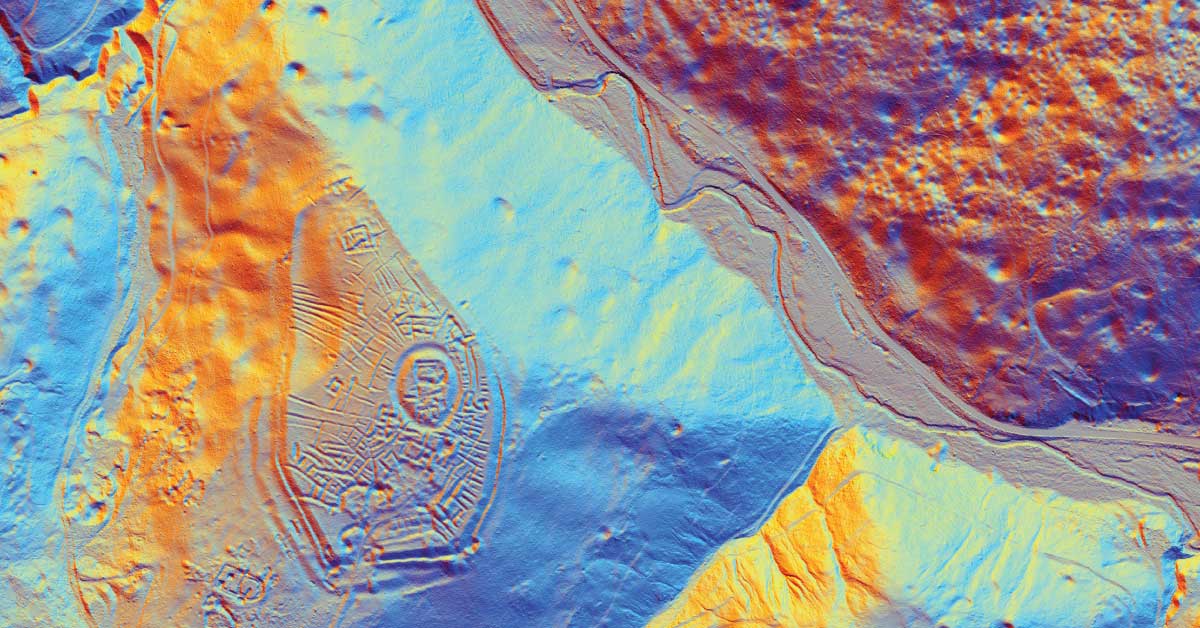
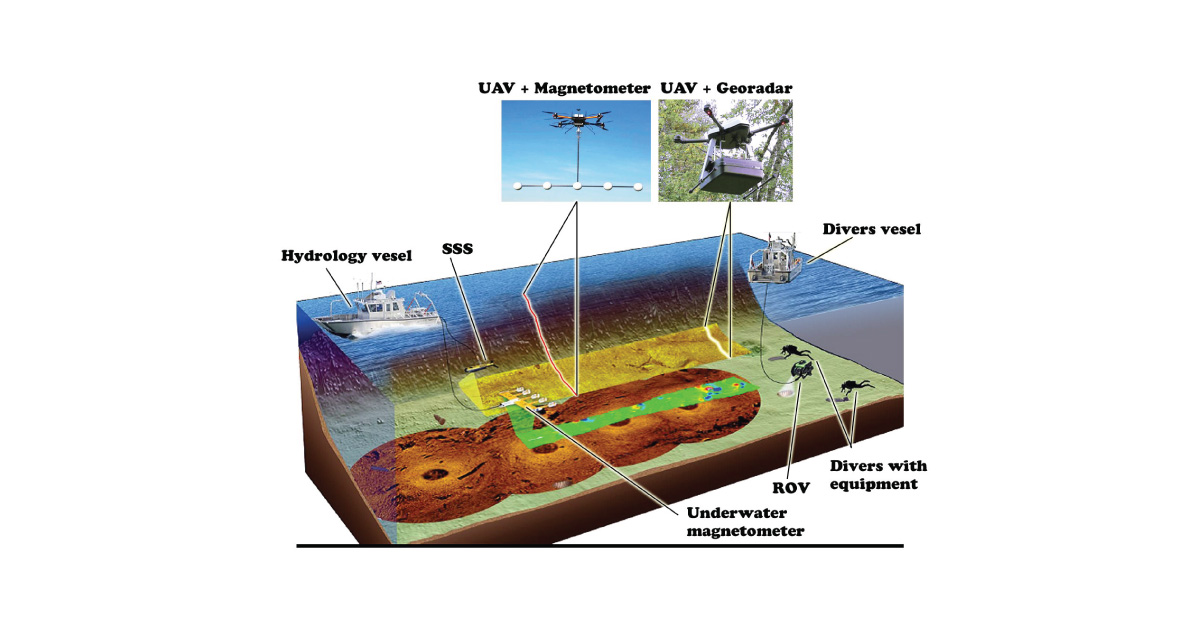
Digital topography represents geometric representation of spatial forms mapped according to corresponding geodetic and cartographic standards. Recent expansion of geographic information systems (GIS) and their tools has enabled geoscientists to visualise the Earth’s surface in three dimensions using digital topography. Digital topographic map is formed for a specific area defined by terms of reference. Digital topographic map can be created in combination with digital cadastre map, which then gives a cadastre-topographic map for a specific area.
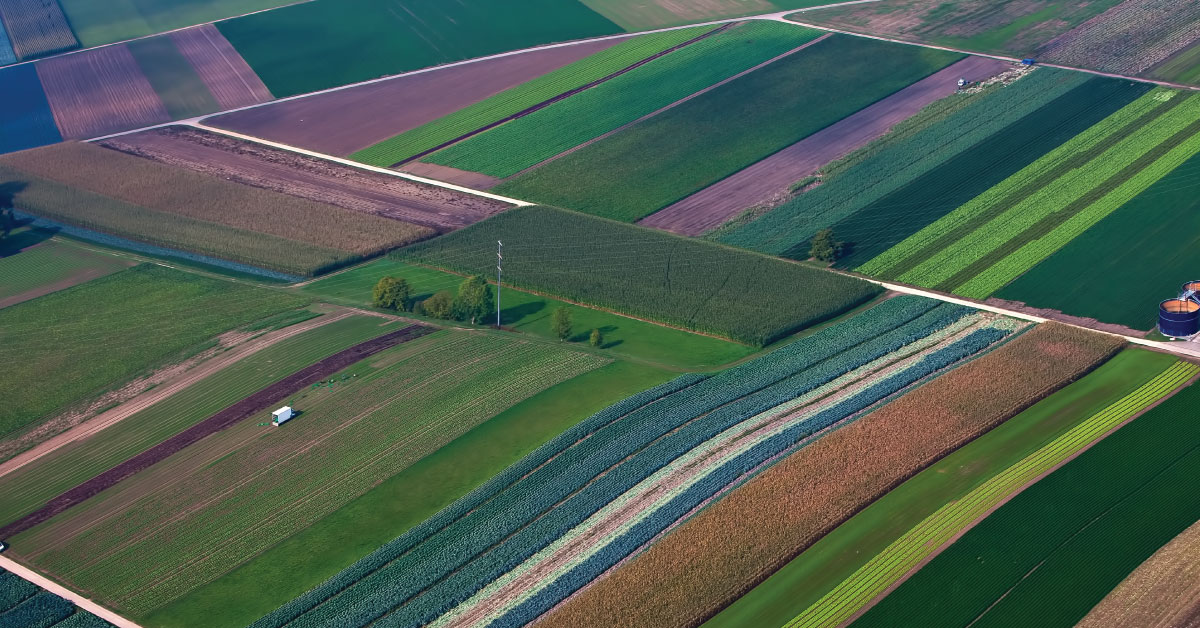
Topography is a field of geoscience concerned with describing and studying Earth’s surface, its relief and physical and geographic features, elevations and inclinations. As a science, it is of great importance in the sphere of spatial planning, in agriculture, as well as hydrology, since it helps determine drainage divides, marking water courses and bodies of water. Internationally accepted symbols for specific objects and social inventory are cartographic or topographic signs. Maps that give topographic representations of landscapes are called topographic maps.
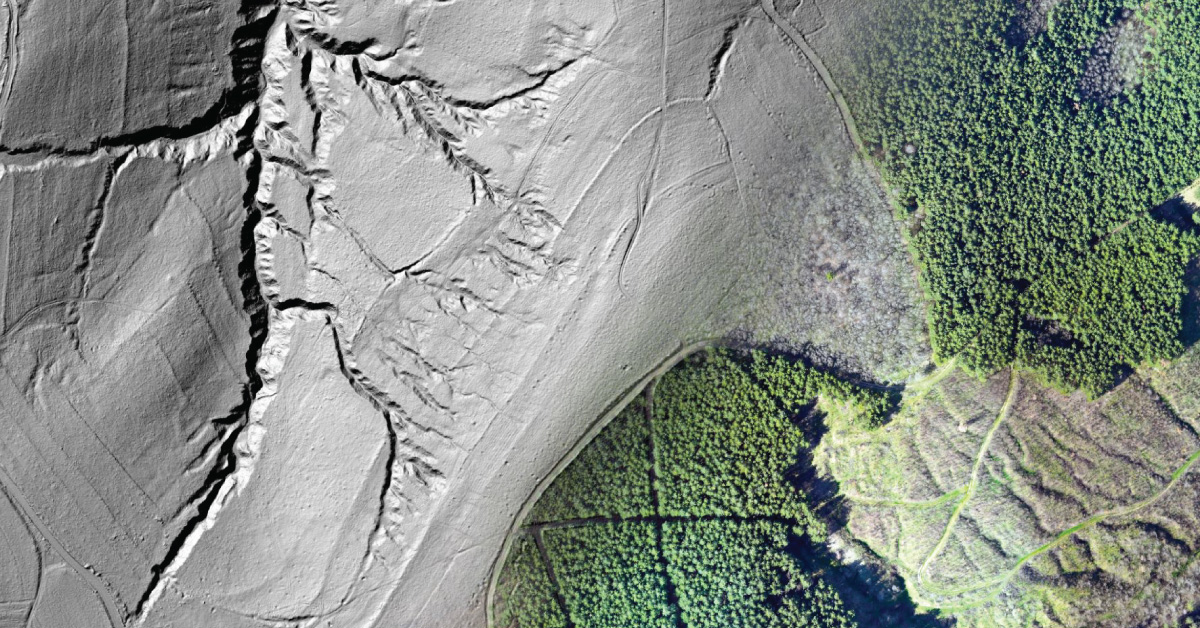
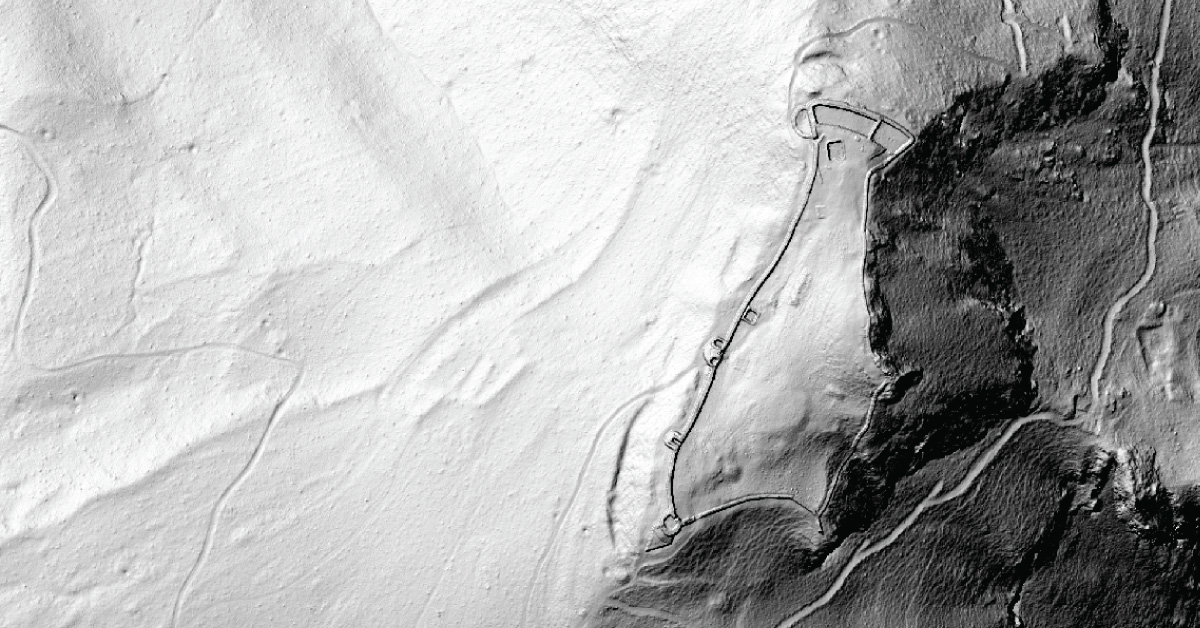
Topography of landscape can refer to the shape and characteristics of the surface, as well as its description (especially description of the maps). In a narrow sense, topography implies recording of relief or terrain, the three-dimensional quality of the surface, and the identification of specific landforms, which is also known as geomorphometry. In modern usage, this involves generation of elevation data in digital form (DEM). It is often considered to include the graphic representation of the landforms on a map using a variety of techniques, including contour lines, hypsometric tints, and relief shading.
Realisation of projects with high level of detail requires updated and quality geodetic survey maps that meet the requirements of modern planning. In the process of making urban and other spatial plans, as well as all the work phases in civil engineering, architecture and urban planning, geodesy and cartography have their applications, starting with the production of project concept, survey and realisation of the project on site, as well as monitoring surveying operation. Conventional method of producing geodetic survey and topographic maps mostly related to cadastre and cadastre-topographic plans which are not sufficiently updated to fully fulfil the users’ specific needs. The very intensive development of geoinformation technologies is creating the conditions for production of geodetic survey maps that will meet increasingly more complex demands of planning.
It is now possible to use different data sources and extract from them a wide range of information. All that, of course, accompanied by a significant improvement of the system’s performance. This is the reason for the switchover from conventional methods to new technologies for production of digital topographic maps. Designed goals for the switchover to the modern operation mode in the field of spatial information technologies are: acquiring quality digital maps for production of all kinds of urban planning and other projects, significant money, time and resource saving, but with necessary initial investment, implementation of modern technologies in the process of spatial panning. Accuracy of geodetic-cartographic documentation corresponds to the time of its creation, which bears the seal of the development of technology of that time. With modern development of computer technology, application of new technologies and equipment in planning and realisation of geodetic works satisfies the need for precise and up-to-date geodetic-cartographic documentation for the production of spatial and urban plans, designing, construction and other technical needs.
Depending on the required level of detail and the use of topographic map, adequate data acquisition method is also selected.